My advice on turning a presentation into a story is through the lens of a scientist. However, the tips below apply for almost any field!
Science has a communication problem. After attending the AAAS meeting, it was clear that great efforts were being spent to improve this. Scrolling through my Twitter feed, I would scan tweet after tweet with suggestions on how to improve one’s presentations. One tip, popping up over and over again amongst tweets, was the use of stories. In fact, the story has captured so much attention that at the first Citizen Science Conference, they had whole sessions where people told stories instead of presenting talks. Since then, I’ve made it a goal to transform any presentation into a story.
Telling stories may scare scientists. During graduate school, your advisor immediately crossed out any writing that appeared flowery, creative, and unnecessary. Science is all about the facts and concise, while stories on the other hand, are often equated with fantasy, drama, and imagination.
How then, are scientists, who are so coached to report facts and data, supposed to turn a scientific presentation into a story? A lot of people are probably dubious that the two can even mix, worrying that it may compromise scientific truth. Science and storytelling are not mutually exclusive, but when done right, complementary. In order to do it well though, it must be thought through.

Before I discuss what a science story is, let me address what a story is not. Just because your presentation does not use PowerPoint or visuals does not mean you are telling a story. Giving a presentation without text on slides is not a story. Describing a situation or telling anecdotes is also not a story. Just because you say “today, I am going to tell you a story,” does not mean it is a story (or at least a good one). Remember when you had to write your own short stories? The principles you learned in your middle school English class are exactly what you need to turn your presentation into a story.
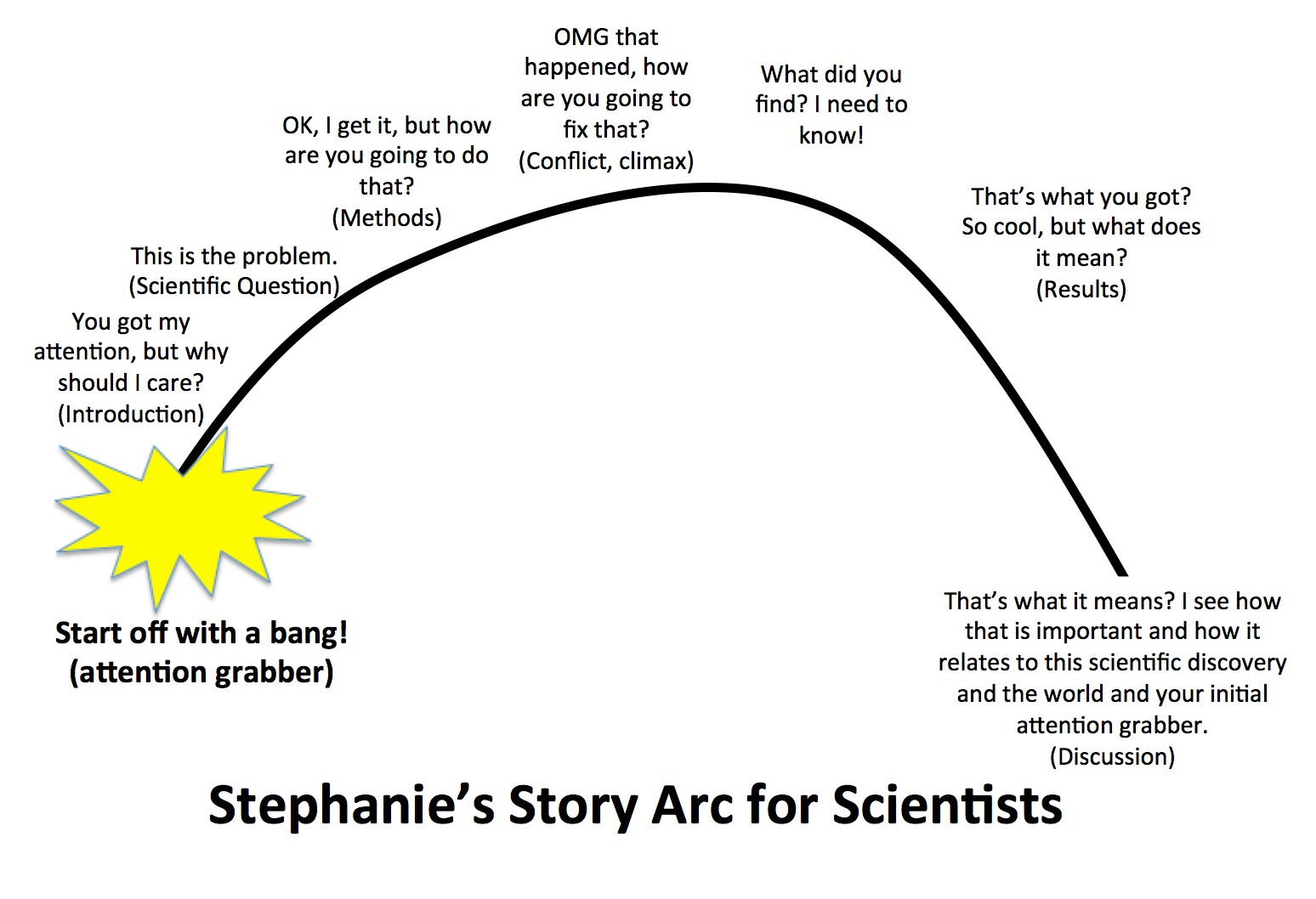
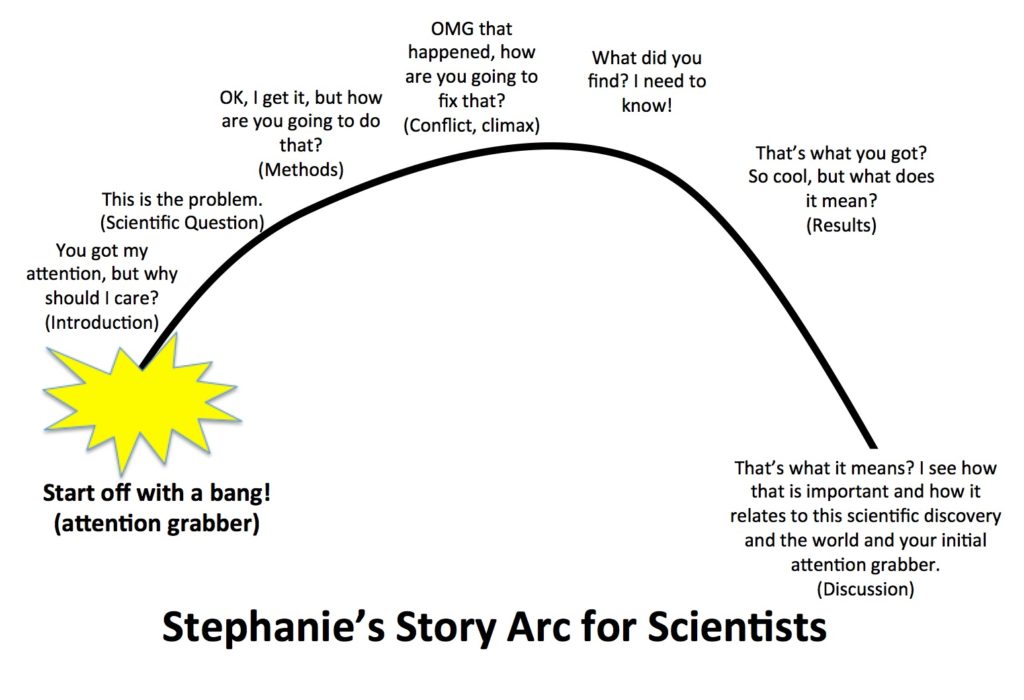
Setting
- Setting the stage – Just like a good story, you need to set the stage for your science. There are many ways to do this, but the most important thing is to get a hook of some sort, spark their interest, and make your audience care. One of the best ways to do this is by relating the broader picture of your research to a real connection in your audience’s lives. For one of my talks at the museum on cooperative behavior on elephants, I immediately make the audience think of their own families, and a time that they needed help by showing them a photo of a baby elephant stuck in the mud and its family members helping it out. This is something that kids and adults both can grasp. Think big and broad. Watch TED talks to get some ideas on how to do this. Your opening and closing slides are your most important. Don’t start by presenting an outline or telling people where you are going to go. Just go there.
- Setting the scene – In addition to hooking us in, you also need to take us away. Where are we in this story? This location may change as the story progresses and depending on how large of a story you are telling. Using my dissertation research as an example, if I only discuss one chapter (e.g. 12 min conference talk), it may mostly occur in the savannas watching forest elephants in Gabon. In this case and in many ecological studies, the park and habitat are extremely important to the story of forest elephant sociality. If I were telling the whole dissertation story (e.g. 50 min seminar), the scene would change from the open savannas to the looking at sequences in the lab.

Plot
- This is the most essential component to turn your presentation into a story. First, a problem needs to be introduced. This is inherent in science. As a scientist, you are trying to answer some question (e.g. problem). Without your study, the problem will never be solved (unless someone else studies it). After the broader introduction and setting, start to transition into the details of your study, and why there is a specific problem. Make sure to include why it is essential to solve it and add a sense of urgency to solve it.
Characters
- This may sound phony, but your science does have characters. In fact, you are the biggest one – the protagonist. You are the one solving the biggest problem (your scientific question). Other characters can include collaborators* (helping you solve a problem you couldn’t on your own), your study species (they might be cooperative or difficult for your question), and you can even have villains. (Note – for your scientific career, do not identify real people as villains!) Villains can arise in other forms: weather, something breaks, all of your treatments fail, or your study species won’t cooperate. These characters definitely add drama.
Arc, Finale, and Full Circle
- This is an extension of plot, but needs to be pointed out. Your story needs to be built up. We need to have a sense of suspense. What are the results? What did you find? Build up the drama to this and not in a phony way. Your enthusiasm (which I hope you should have for your research) should make this real so the audience also really wants to find out what you found. When you finish, like the introduction, you need to discuss the importance of your science and tie it back with introductory material. Make your story come full circle if you can by relating it to your opener. Have this be an impactful slide that the audience will remember.
That’s it! You already have all of the material you need from your own research. You just need to reframe the way you have been thinking about your study to presentation into a story. For design tools to make your powerpoint slides look beautiful and help with your story, check out Canva.
*As mentioned before, your first and last slide are the most important slides. While a lot of people helped you along the way, acknowledgement slides are just a long list of peoples’ names to look at while you are asking questions (in other words, a really boring slide). It’s much better to integrate their efforts throughout the talk or honestly just leave it out. I never include acknowledgements in my slides anymore.
**This blog was originally posted on the Wildlife SNPits.
SaveSave
SaveSave
SaveSave
SaveSave
SaveSave
SaveSave
SaveSave
SaveSave
SaveSave
Love this post? Share it with friends!